Web Browser is used to access information resources like websites, images, videos from the World Wide Wave(WWW). Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Safari, Firefox are some of the commonly used browsers. Since these browsers are installed not only on Computers but also on cell phones, tablets and IoTs, it has become one of the most used channel for cyber attack.
Therefore, it is critical to understand the importance of using these browsers in a secure manner.
By default, most of the browsers come with minimum security features enabled, thus creating an easy platform for hacker to launch malicious code to get control of your device.
There is an increase in number of threats taking advantage of vulnerabilities present in the web browsers through use of malicious websites. Users not realising the the risk of clicking on links and leaving the web browsers configured insecurely make the work of malicious actors easier.
Following are simple actions that end users can take to securely configure their browsers to safeguard their devices.
1. Keep the browser Up to date:
- Browser vendors release security updates periodically to address vulnerabilities using which an attacker could exploit your browser to gain complete access to your device using readily available exploits. Thus, it’s important to patch your browser as soon as the vendor releases update.
- If you are providing any information(username, Password, Date of Birth, ID card number, etc…) online make sure your communication is happening over secure channel.Check for a lock sign with green address bar, like the one below.
- Install HTTPS Everywhere plugin.
2. Review the security setting periodically
- Block reported Malicious sites:
Enable this feature to prevent accidentally visiting the malicious site resulting to device compromise.
- Adds and Pop up:
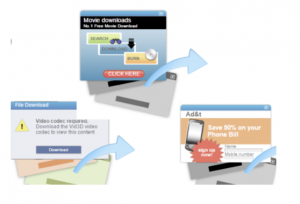 Be wary of the advertisements and pop-ups as you visited online sites, many times malicious codes are injected in them with exploits to gain access to your device. Do Not click on them as far as possible, unless you are sure of its authenticity. Install Ad Blockers on your browsers.
Be wary of the advertisements and pop-ups as you visited online sites, many times malicious codes are injected in them with exploits to gain access to your device. Do Not click on them as far as possible, unless you are sure of its authenticity. Install Ad Blockers on your browsers.
- Plugins/Add-Ons :
Malicious actors might have installed plugins while you clicked on some links or visited infected sites. Review the list of installed plugins and add-ons and uninstall them if no more used or if you notice some of them which you never installed.
- Cookie:
Disable entirely, or only enable when you visit a trusted site which requires them
- JavaScript:
Block from running automatically, enable it only for trusted websites and/or have the browser ask you each time a site wants to run a script
-
- Enable “Protect you and your device from dangerous sites” or similar feature.
- Do Not allow your browser to remember password.
- Enable browser’s “private-browsing” or “do-not-track” features
- Camera / microphone usage :
Block from running automatically or enable “ ask each time a website wants to use Camera/microphone” feature.
For details on security setting for each of the browsers, please visit:
- Microsoft Edge: https://windows-10-microsoft-edge-and-privacy
- Internet Explorer:. https://windows-internet-explorer-11-change-security-privacy-settings
- Firefox: https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/products/firefox/privacy-and-security
- Safari:. https://support.apple.com/kb/PH21449?locale=en_US
Reference:
- http://www.infosecawareness.in/infosec-concept/browser-security
- https://www.safecomputing.umich.edu/protect-yourself/be-safe-online/web-browser-security-and-privacy
- http://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/info/getstarted/Web-Browser-Security
- https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/browser-security-guidance-introduction/browser-security-guidance-introduction
- https://www.us-cert.gov/publications/securing-your-web-browser

